VMware’s NSX, also known as NSX-T, is a Software-Defined Networking (SDN) solution. SDNs allow IT administrators to create networking components in software rather than hardware. This results in significantly cheaper and faster deployment of network solutions.
Transitioning to a software-defined datacenter skips the time-consuming procurement and physical implementation steps, which enables teams to react faster to new challenges and projects required by the business. Here, we’ll take an in-depth look at NSX and the role it plays in the transition to software-defined infrastructure.
Components of VMware NSX
NSX is an enterprise-ready network solution, and as you’d expect from such a product, has many features and components.
Depending on your license, NSX features include:
- Distributed Routing
- Centralized Firewalls
- Layer 2 Switching (over layer 3)
- Feature-rich load balancing
- Site-to-site and remote access VPNs
- Distributed Intrusion Detection and Intrusion Protection
- Micro-segmentation
- Extend On-Prem Networking to the Cloud for Consistency
VMware NSX configuration simplicity
From a configuration perspective, software-defined networking with NSX isn’t complicated. In fact, a network engineer comfortable with hardware appliances will find many aspects of NSX familiar. This is because the same networking functions provided by traditional appliances are available with NSX, just delivered in a modern way.
For example, with NSX you still define firewall rules, but in addition to source and destination IP addresses, you can specify virtual machine objects. Further, NSX functionality, including firewall rules, is automatically distributed between ESXi hosts. This means that if one ESXi host goes down your network is not compromised.
Use cases for VMware NSX
NSX has a variety of benefits that can help streamline and scale your network operations. Because of its features and functionality, the four main use cases for NSX are:
- Application Delivery
- NSX connects with VMware’s vRealize Automation Suite, enabling a blueprint-based approach for delivering applications.
- A single blueprint can define your networks, firewall rules, and application requirements, all of which can be deployed in just a few clicks.
- Containerisation
- Containerization and the use of tools like Kubernetes are becoming commonplace for many organizations. NSX provides a full-stack network suite for enabling network features and security for containers.
- Security
- NSX enables the rapid creation of DMZs in software. Applications can be further isolated with micro-segmentation which allows you to create firewall rules between virtual machines, even if they are on the same network.
- Load Balancing
- Software-defined load balancers can have large savings, both from a cost and time perspective. NSX load balancers take seconds to deploy and such services can be distributed logically between different sites for the best possible availability.
What are VMware NSX’s key capabilities?
NSX is an incredibly smart SDN solution, but what are the key technical capabilities?
NSX is an abstraction of the hardware layer. All NSX services run in software so components such as a VPN or firewall can be created in just a few seconds.
Another benefit of NSX running in software is that it can be backed up and restored quickly. Further, all NSX services are distributed. Key NSX components run on ESXi hosts ensuring reliable distribution and scalability of all network and security infrastructure.
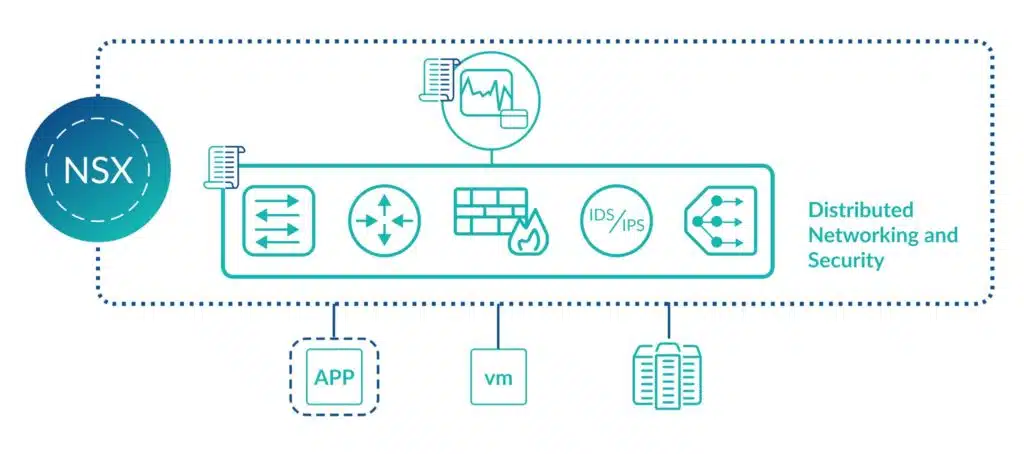
Diving deeper into the technical aspects of NSX
Now that we understand the fundamentals of NSX, we can take a closer look at the technical details. Below, we’ll describe how key components of NSX work from a technical perspective.

“The CloudBolt team has been with us on this journey to self-service… This level of partnership and shared direction has enabled Home Depot to move faster, move further and continuously enhance our offerings to our Development Team customers.”
– Kevin Priest, The Home Depot
- Firewalls. NSX allows you to create firewalls and related functions. NSX is policy and object-based. This means you can select objects such as containers, hosts, and virtual machines to create firewall rules. If the IP address of one of these components changes, then the rule is automatically updated. As a result, you save time and reduce the possibility of human error.
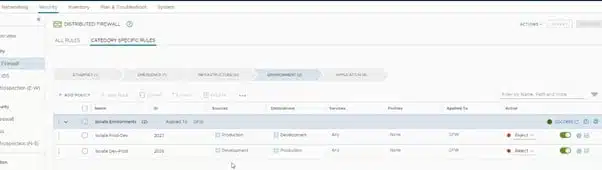
- Load Balancing. Load balancing your applications for the best availability is key. NSX supports load balancing features from layer 4 to layer 7. SSL offloading, passthrough, and health checks are all included. You can also set up application rules and traffic manipulation via both the graphical user interface and command-line interface.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). NSX supports all common VPNs. This includes site-to-site and client-based VPNs with all the usual cipher and encryption options.
- API. NSX comes with a fully functional API. While not every administrator will utilize the API, it can be incredibly powerful. This is especially true if you use a 3rd party tool that can hook into NSX’s capabilities.
- Micro-Segmentation. Micro-segmentation is one of the most important security features in NSX. This technology is useful because it allows you to firewall network traffic between virtual machines (a.k.a. “East-West traffic”) in a variety of scenarios. This includes when the virtual machines are on the same network, located on different hosts, or even in different regions of the world.
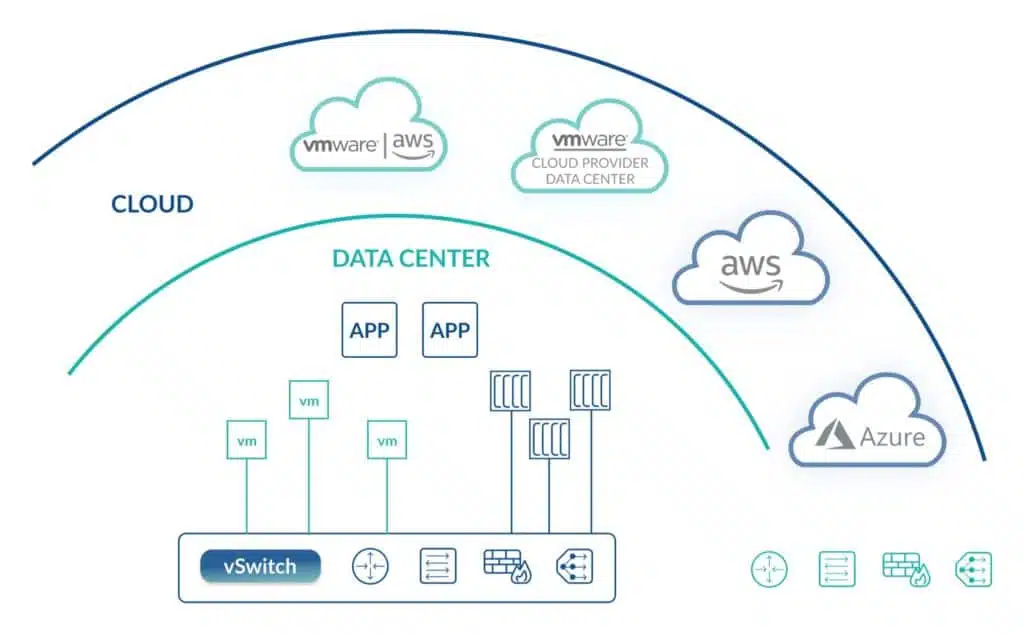
- Multi-cloud Networking. Traditional network hardware has no cloud capability, but with NSX it’s possible to connect NSX to your public cloud solutions. For example, you can manage your public and private cloud data center networking from NSX in a single pane of glass.
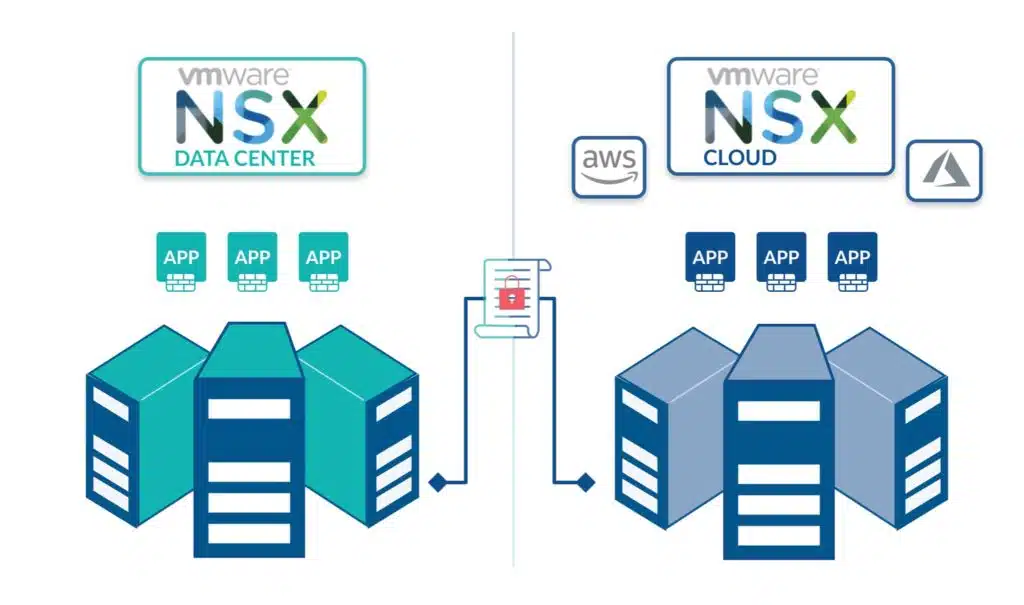
- Automation. We’ve briefly discussed the API option in NSX, but you can also extend VMware vRealize Automation to automate the configuration of VPNs, firewall rules, load balancers, and other NSX features. NSX also supports AWS Terraform and there are feature-rich PowerShell cmdlets for NSX too.
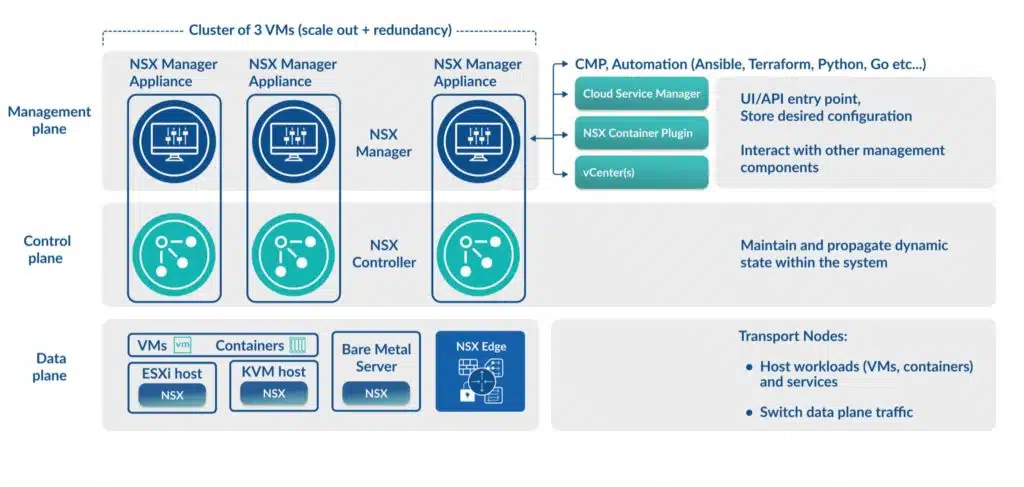
NSX-T Components and Topology
NSX has a simplified topology that tightly integrates with VMware’s ESXi hypervisor as well as other hypervisors. The key components to an NSX deployment are the management plane, control plane, and data plane. Here, we’ll take a closer look at each.
NSX management plane
This layer includes the NSX Manager appliance. NSX Manager is the user interface for NSX. Its look and feel are similar to vCenter Server, but instead of managing hypervisor hosts and virtual machines, NSX Manager is responsible for managing the networking and security components of NSX.
NSX Manager is also the entry point for API requests and it integrates with other management solutions, including vCenter Server to discover information about the virtual machines in the network.
NSX control plane
The control pane is home to a number of NSX Controllers. These are virtual machines that operate in a cluster and manage the configuration state of networking and security components. Traffic does not flow through the controllers as they are used for configuration and system state management only.
NSX data plane
The NSX Data Plane is where VMs and containers are situated, typically on a hypervisor such as ESXi or KVM. The data plane is responsible for the forwarding and transformation of IP packets that are derived from the control plane. It’s the NSX virtual switch that’s installed on the participating hypervisors that does much of the switching work for NSX.
VMware NSX Licensing
The NSX features you can use depend on the license model which you select.
The table below displays key NSX features and their license requirements:
| NSX Feature | Standard | Professional | Advanced | Enterprise Plus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Switching and Routing | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Stateful Gateway Firewall | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| NAT Gateway | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Layer 2 Bridge to Physical Layer | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| VMware vRealize Integration | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| L2 and L3 Load Balancers | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| NSX Cloud for AWS and Azure Support | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Container Networking and Security | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Federation | No | No | No | Yes |
| VM-to-VM Traffic Flow Analysis | No | No | No | Yes |
Getting Started with NSX-T
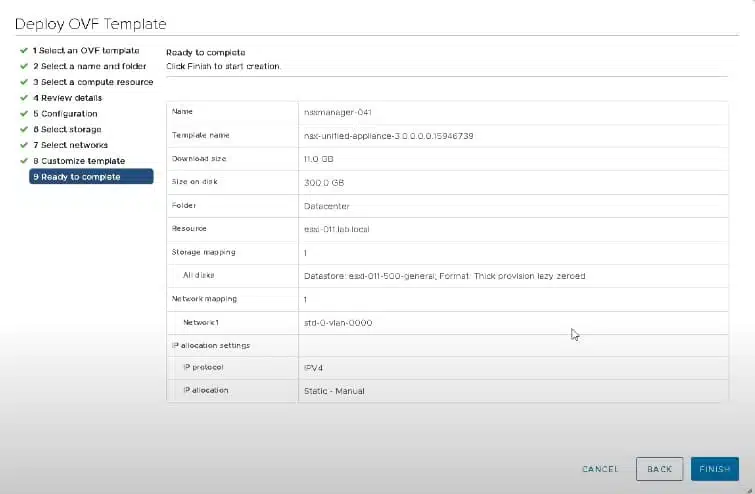
The installation and deployment of NSX-T is straightforward. The main component and starting point for NSX is the NSX Manager. NSX Manager is provided as a simple OVF file that you can deploy directly into your vCenter Server.
Simply log in to your vCenter Server via the HTML5 interface and create a new virtual machine from the OVF. Follow the wizard and enter the requested information to deploy the appliance.
Once NSX Manager is deployed you can log in to the IP address or hostname specified in the wizard and begin the remainder of the NSX deployment and configuration
Don’t forget, as is the case with most technical solutions, the key to success is in the planning. Once NSX Manager is deployed, you’ll want to complete the next steps:
- Deploy an NSX Manager Cluster
- Install NSX Edges
- Create NSX Edge Cluster
- Create Transport Zones
- Create Transport Nodes
Fortunately, VMware provides a free design guide for NSX-T which is available here.
Once you have designed your deployment, it’s time to install and configure everything. The official documentation for NSX can be found here and you can use that guide as a baseline for your installation
Other ways to get started with NSX
If you want to learn more before you get hands-on with NSX, VMware offers a variety of resources to help you do just that.
- Official Training & Certification
- VMware’s official training is some of the best in the industry, certified VMware Instructors conduct all training sessions either in-person or in a remote setting.
- There are also self-paced training options which are pre-recorded sessions that you can follow at your own pace and time.
- Free Hands-on Labs
- VMware has many free-to-use labs. These are real systems that you can log in to and interact with.
- The VMware Hands-on Labs allow you to deploy NSX and complete various configuration tasks. They all include a manual to guide you through the system and help you with scenarios.
To get started with the labs, visit https://hol.vmware.com
- Complimentary NSX eBook
- For more on NSX and how to get started, download the free NSX VMware eBook.
Related Blogs
The End of Manual Optimization: Why We Acquired StormForge
Today is a big day for CloudBolt—we’ve officially announced our acquisition of StormForge. This marks a major milestone for us…