Cloud service providers need customers to consume as much compute capacity as possible to enhance their platform’s efficiency. With price being a major contributing factor, they need an innovative costing model. One that drives high utilization and offers the vendor some flexibility. Azure Spot VMs is an Azure feature that provides this benefit. Its pricing delivers significant discounts to customers while giving Microsoft the agility it needs to rapidly reassign or reclaim resources on its public cloud platform.
What is Azure Spot?
Azure Spot VMs is an Azure feature that allows you to take advantage of the platform’s unused capacity. Using this option helps Microsoft drive efficiencies and realize the returns needed on their economies of scale. Subscribers get Azure Spot VMs at a significantly discounted rate for selecting this feature, making it a win-win for both parties. This option can help Azure customers lower their cloud computing costs up to 90 percent discount in some cases.
Pricing and eviction are the only differences between Azure Spot VMs and regular virtual machines. You will learn about evictions in this article. As far as performance, vCPU, memory, and network, the services are identical. Azure Spot VMs also offer the same security, scalability, and flexibility. You commission them on the same virtual network, protect them with Network Security Groups, and you can load balance and scale them using Virtual Machine Scale Sets. The core difference between Azure Spot VMs and regular virtual machines is uninterrupted availability. As you are getting a significant discount for consuming Azure’s unused capacity, when Microsoft needs it back, they re-allocate the spot resources to customers paying full price. This is what is defined as Eviction.
Use Cases for Azure Spot VMs
Although high-availability is not a core feature of Azure Spot VMs, other workload types pair very well with this consumption pricing model. The ideal use case for a Spot VM is a service or application where an interruption is acceptable. However, the workload selected must also not need to complete within a given timeframe.
High-Performance Computing Scenarios
Suppose you have a workload that uses multiple CPU or GPU-based computers to solve complex mathematical algorithms. In that case, the Azure Spot VM pricing model is the perfect balance between performance and price. As these tasks typically involve long periods where users wait for calculations to complete, any interruption will not diminish the user experience. It may take a while longer, but as the user is not interacting with the service, the break will not impact production.
Batch Processing Jobs
Like high-performance computing scenarios, batch processing jobs also fit the use case for Azure Spot VMs. These workloads follow the same approach where a workflow submits a task to a computing resource for execution. If these batch processing jobs take some time to complete, assigning them to an Azure Spot VM instance will lower the cost. As there is no interaction while the batch runs the process, an interruption will not impact your user’s experience. As mentioned previously, if the batch run timing is mission-critical, commissioning a standard VM would be a better option.
Dev/Test Environments
Another ideal use case for Azure Spot VMs is a development or test scenario. Typically, these environments do not require high-availability. They are also usually at the bottom of the critical list when it comes to IT budgets. Often organizations do not spin up development or test environments in the cloud to save cost. Legacy on-premise hardware is the usual location for these non-critical services. However, having these environments on-prem and your production on Azure is not ideal. Not only does it counter the best practice recommendation that all settings should be identical. It also creates unnecessary complexity in your DevOps environment when you need to deploy fixes or releases. By leveraging Azure Spot VM pricing, you can align development, test, and production while achieving a significant discount.
Other Azure Spot VM Use Cases
In addition to the examples listed above, a few other workloads may make ideal candidates for Azure Spot VMs. However, depending on the service they host or process, you need to consider the impact should an interruption occur.
Stateless: Single-use, stateless applications like web servers that host static content are also candidates for Azure Spot VMs. However, depending on the hosted content, this use case may not be ideal. For example, if your public website consumes static content, you would not want visitors to experience your site without any CSS, images, or JavaScript. A more suitable use case would be a scenario where your development team needs to host these data types for a test environment.
Temporary Services: In some instances, you may need to spin up a virtual machine for a short amount of time. If you are comfortable running the risk, a Spot VM may be a suitable candidate. Unfortunately, there is no way to predict if or when Azure may need its unused capacity back. For this usage scenario, the level of risk equals the amount of time you need the service online.

See the best multi-cloud management solution on the market, and when you book & attend your CloudBolt demo we’ll send you a $75 Amazon Gift Card.
Instance Configuration Options and Cost Optimizations
Azure Spot VMs can help you reduce your Azure compute spend by offering significant discounts for consuming unused capacity. However, in addition to this feature, they also help you save costs by setting a maximum price.
Instance Configuration Options
A spot VM may be running, stopped, deallocated, or transitioning between two states. The diagram below summarizes the states that a spot VM may be in:
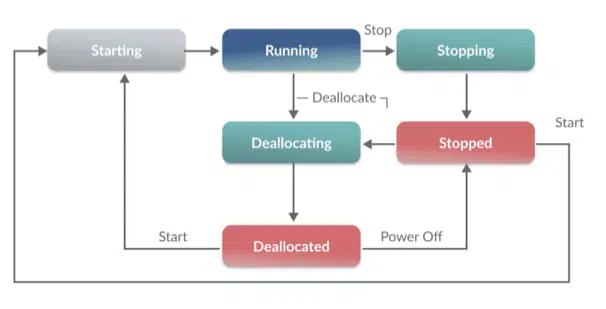
The transitions from state to state are managed by the configuration options. The table below provided by Microsoft details the various configuration options and the outcomes of each.
| Option | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Max price is set to >= the current price | VM deployed if capacity and quota are available. |
| Max price set to < the current price | VM not deployed. You will get an error message that the max price needs to be >= current price. |
| Restarting a stop/deallocate VM if the max price is >= the current price | If capacity and quota are available, then the VM is deployed. |
| The price for the VM has gone up and is now > the max price | The VM gets evicted. You get a 30-second notification before actual eviction. |
| After the eviction, the price for the VM goes back to being < the max price | Azure will not automatically restart the VM. You can restart the VM yourself, and Azure will charge it at the current price. |
| If the max price is set to -1 | Azure will not evict the VM for pricing reasons. The maximum would be the price for standard VMs. Azure will never charge you above the standard price. |
| Changing the max price | You need to deallocate the VM to change the max price. Deallocate the VM, set a new max price, then update the VM. |
Eviction Options
When Azure evicts your Spot VM, the service will not notify you unless you opt-in to receive in-VM notifications via Azure Scheduled Events. Should Microsoft need capacity, or the spot price exceeds the maximum price, the eviction process only gives you 30 seconds’ notice. This minimal timeframe endorses the previous recommendations that you need to select the workloads you deploy on Azure Spot VM instances carefully.
When you configure an Azure Spot VM instance, you select the eviction type and policy during the virtual machine creation process. There are two eviction types.
Eviction Types
Capacity Only: If you select this eviction type, Azure will only evict your VM when it needs capacity. In this instance, the Spot VM’s maximum price is the regular price for a standard virtual machine on your subscription. As the price you pay for your VM may vary, this option is not ideal when you are working with a strict budget. However, the probability of Azure evicting your Spot VM is lower.
Price or Capacity: If you choose Price or Capacity as your eviction type, Azure will evict your VM when the spot price exceeds the threshold you set during the configuration phase. It will also evict it if it needs capacity. This eviction type is best suited for workloads that have a set budget. Consequently, it also has a higher eviction probability.
Eviction Policies
The Azure Spot VM eviction policy dictates Azure’s actions when your Spot VM exceeds the capacity or maximum price threshold. Currently, there are two configurable eviction policies: Stop/Deallocate and Delete. If you opt for the Stop/Deallocate option, you must bear in mind that Azure will still charge you for the disk storage. Azure Spot VM pricing only applies to the compute cost of the VM.

|
Platform
|
Multi Cloud Integrations
|
Cost Management
|
Security & Compliance
|
Provisioning Automation
|
Automated Discovery
|
Infrastructure Testing
|
Collaborative Exchange
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CloudHealth
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
||||
|
Morpheus
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
||||
|
CloudBolt
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
Azure Spot VM Limitations
VM Series Restrictions
The Azure Spot VM pricing model does not support every Azure virtual machine size. It excludes VMs configured to use the B-Series. Spot instance pricing is also not available for promotional VMs of any size, such as the Dv2, NV, NC, and H promo offers.
Subscription Restrictions
All regular subscriptions offer Azure Spot VM pricing. However, this offer excludes any benefit or free subscriptions. These include Azure subscriptions linked to an MSDN or Partner agreement. Azure Spot VM pricing also excludes Microsoft’s free Azure credit when you sign up as a new Pay-As-You-Go customer. Supported subscriptions include Enterprise Agreements, Pay-As-You-Go (after the credit has expired), and Cloud Service Provider.
Technology Restrictions
Azure Spot VMs do not support ephemeral disks, which Azure creates on the local virtual machine storage. If you want to qualify for Spot VM pricing, you would need to configure your VM to use the standard Azure remote storage. The other technology restriction that applies to Azure Spot VMs is conversion. You cannot convert a Spot VM to a regular VM. Similarly, you cannot convert a regular VM to a Spot VM either. If you want to migrate your compute resources from spot to regular, or vice versa, you need to create a new VM and attach the existing disk.
Auto Start Caveat
There is also an operational limitation when using an Azure Spot VM. When Azure stops and deallocates your virtual machine, it does not start up automatically when capacity returns. Even though you can opt-in to receive a notification using Azure Scheduled Events as mentioned earlier, you would still need to restart it manually. However, you could automate this manual process with PowerShell and utilize Azure Automation, a Function App, or a Logic App.
Pricing Comparisons
Spot VM pricing differs for each region and SKU. If you opt for the Price or Capacity eviction type, the savings could be even lower, assuming that Microsoft accepts the price at the time and has the capacity.
The table below is an indication of the level of savings on offer. These figures represent the East US region. However, as mentioned previously, they are indicative only.
| VM Size | Resources | Regular Cost | Spot Cost | Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2v3 | 2vCPUs 8GB | 0.209 per hour | 0.012 per hour | 95% |
| D8sv3 | 8vCPUs 32GB | 0.836 per hour | 0.108 per hour | 87% |
| D2v4 | 2vCPUs 8GB | 0.204 per hour | 0.012 per hour | 95% |
| D8sv4 | 8vCPUs 32GB | 0.816 per hour | 0.488 per hour | 60% |
| E4sv4 | 4vCPUs 32GB | 0.464 per hour | 0.032 per hour | 94% |
| E8sv4 | 8vCPUs 64GB | 0.928 per hour | 0.064 per hour | 94% |
| F4sv2 | 4vCPUs 8GB | 0.396 per hour | 0.068 per hour | 83% |
| F8v2 | 8vCPUs 16GB | 0.792 per hour | 0.137 per hour | 83% |
The table above clearly illustrates the significant cost savings achievable with Azure Spot VM instances. However, the discount does vary between region and SKU, so you must perform the necessary due diligence before committing.
Cost Saving Versus Increased Risk
Azure Spot VM cost optimization and configuration selection is a trade-off between cost and risk. Considering these scenarios, optimizing cost using Azure Spot VMs requires careful consideration of three factors: the type of workload, budget restrictions, and the acceptable level of risk.
As the potential cost of a Spot VM changes continuously, setting a budget before configuring is important. If you opt for the capacity eviction type, you need to monitor the total spend as costs fluctuate. With the maximum cost option, you fix your budget upfront. However, the total cost depends on the Azure Spot VM price when you commission your virtual machine. Both eviction types also carry a varying level of risk. Depending on the workload, you will need to take the eviction probability and its impact on your organization into account.
Related Blogs
The End of Manual Optimization: Why We Acquired StormForge
Today is a big day for CloudBolt—we’ve officially announced our acquisition of StormForge. This marks a major milestone for us…



